What is Zilliqa?

Speed and efficiency are the desired qualities in blockchain transaction processing. In the blockchain world, the challenge of increasing the number of transactions and speed is known as the problem of scalability. To overcome this, Zilliqa comes with sharding technology to solve the problem of scalability. Not only that, Zilliqa is a large platform that offers a variety of interesting features for crypto users and developers. Check out the full review of Zilliqa in the article below.
- ⛓️ Zilliqa is a blockchain project that aims to address scalability challenges through sharding technology and a consensus mechanism that combines Proof of Work (PoW) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
- 🧑🏻💻 Zilliqa was founded in 2017 by a team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and has since grown into a platform for thousands of decentralized applications (dApps) and over 3700 tokens.
- ✍🏻 The Zilliqa network enables the development and writing of smart contracts through the Scilla programming language, which is designed with security and efficiency in mind.
- ↔️ Zilliqa has a native token, ZIL, which is used for transactions within its ecosystem, including staking, buying and selling NFTs, creating DApps, and fundraising.
- 🆕 On July 5, 2023, Zilliqa successfully upgraded its mainnet to v9.2, introducing several enhancements and new features, including improved interoperability between the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Scilla.
What is Zilliqa?
Zilliqa is a Layer 1 blockchain designed to tackle the scalability challenge, which refers to the need for a cryptocurrency platform capable of processing a high volume of transactions rapidly. Serving as a smart contract platform, Zilliqa enables the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and tokens within its blockchain infrastructure.
Who Founded Zilliqa?



First launched in 2017, Zilliqa was founded by a group of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) consisting of Xinshu Dong, Yaoqi Jia, Amrit Kumar, and Prateek Saxena. After its launch in 2017, the testnet was brought online in March 2018 with a mainnet launch in June 2019.
Zilliqa’s founders saw great potential in blockchain technology but recognized scalability as a significant barrier. As a result, Zilliqa was designed to be a transformative platform capable of supporting thousands of transactions processed in seconds. This scalability solution is achieved through sharding technology. In addition, to ensure the security of its network, Zilliqa uses a consensus mechanism that combines Proof of Work (PoW) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
How Does Zilliqa’s Works?
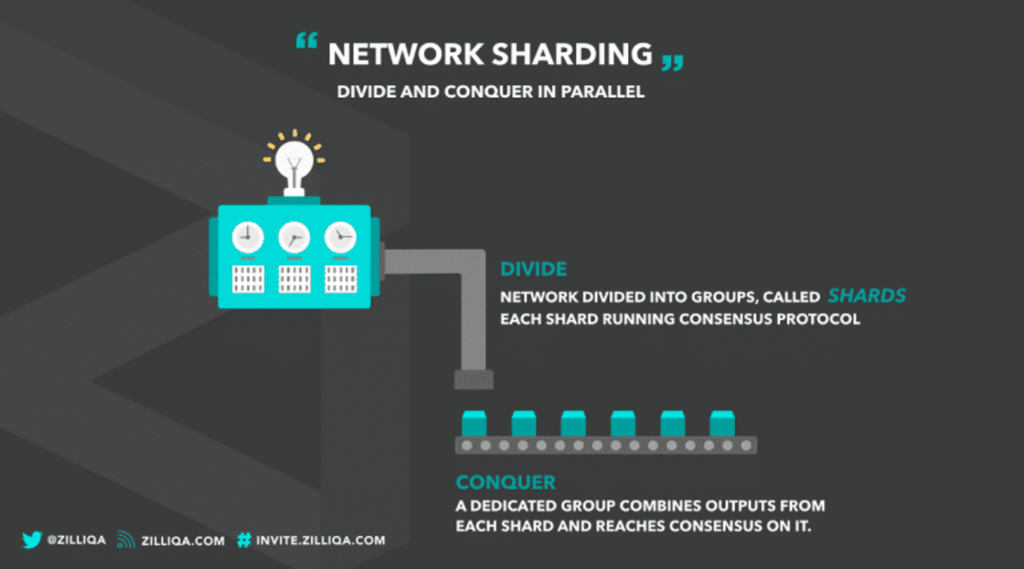
The Zilliqa network consists of two main pillars. The first pillar is transaction processing using sharding technology. The second pillar in Zilliqa is the PoW and PBFT consensus mechanism.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
The second pillar within the Zilliqa network is a modification of the PoW consensus protocol with PBFT. This modification is claimed to save mining costs, including the verification and validation of blockchain transactions.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) is a system capable of avoiding failures caused by the Byzantine General Problem. PBFT is at the core of Zilliqa for implementing governance mechanisms that can keep distributed computer networks in sync. In short, a BFT system can continue to operate even if some nodes fail.
For nodes that can operate the blockchain and vote, the first thing they do is stake ZIL tokens. Anyone with ZIL tokens can operate the network. So, the use of PBFT in the operation of the network is to complicate fraudulent or fake transactions on other nodes. In practice, all nodes must agree on the validity of the new block before it is added. Then, each node receives a small portion of the block reward.
The Zilliqa team claims that modifying PoW and PBFT creates a secure mechanism and allows mining with lower computational costs.
The Advantages of Zilliqa
In addition to sharding and modifying PBFT with PoW consensus, the Zilliqa network includes a smart contract layer that provides many features that make it easy to develop and write smart contract programs.

In practice, however, Zilliqa does not use the term “smart contract” directly but instead uses its own intermediate-level smart contract programming language developed by Zilliqa, known as Scilla (Smart Contract Intermediate-Level Language). Scilla is designed as a programming language that takes into account the security of smart contracts and aims to create new programs, namely decentralized applications that offer a variety of products and services.
As for Scilla, it has four main advantages. These are:
| Science-backed | Scilla is a peer-reviewed smart contract language that supports the world’s most advanced sharded protocol. |
|---|---|
| Fewer security risks | Scilla’s static analysis framework and automatic scanners allow developers to more easily identify common security vulnerabilities. |
| Safer contracts | Its strong type system makes it easier to write bug-free code. |
| Proof of mathematical safety | Scilla is inspired by functional programming languages such as OCaml, making it easy to perform formal verification, the automatic mathematical proof of security properties. |
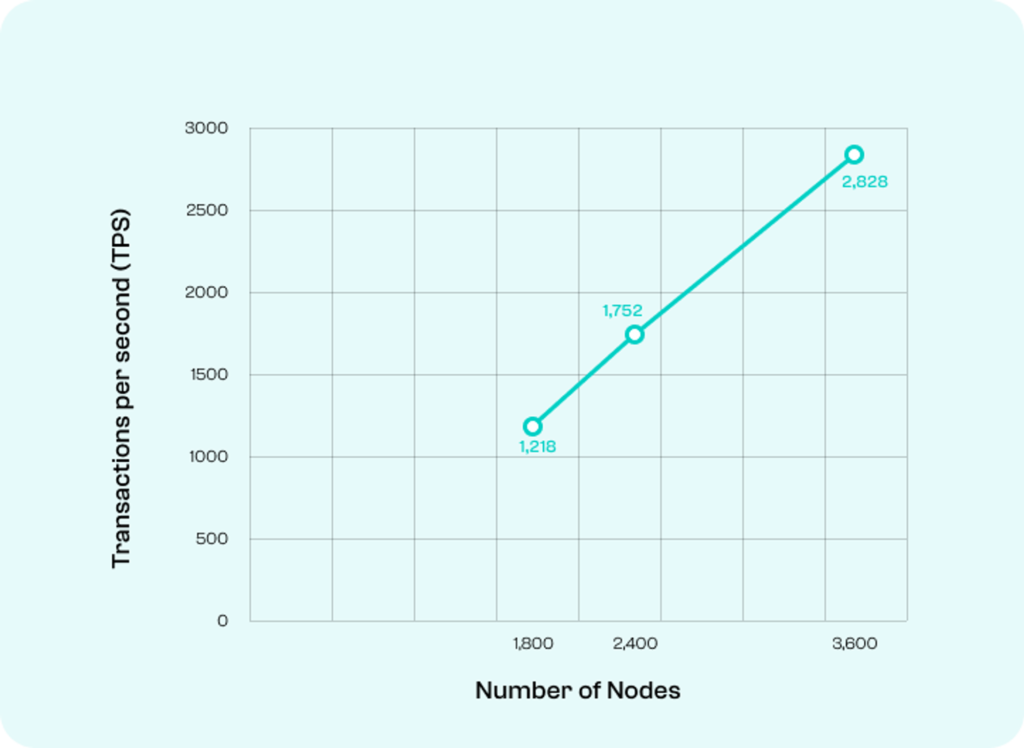
Furthermore, Scilla directly leverages sharding architecture to provide a highly scalable and efficient computing network. Zilliqa is the first layer 1 blockchain to implement sharding. Sharding can process up to thousands of transactions per second. For example, with a total of 3,600 nodes, the Zilliqa network can collectively process 2,828 transactions per second. By implementing sharding technology, Zilliqa is able to solve the scalability problems of Layer 1 networks.
Zilliqa’s Ecosystem

The Zilliqa ecosystem is constantly evolving. Currently, Zilliqa has become a platform for thousands of dApps and more than 3700 tokens available in the Zilliqa ecosystem. In addition, the Zilliqa platform also enables staking and yield farming using ZIL tokens. These native Zilliqa tokens are also used in various fields such as advertising, entertainment, financial services, gaming, and payments.
ZIL Token
In 2017, Zilliqa introduced its ERC-20 token, ZIL. This token serves multiple purposes, including storage, transfer, and staking. As the native token of the Zilliqa blockchain, ZIL is specifically created to facilitate the scalability of decentralized applications, spanning various sectors such as financial services and NFT marketplaces.
By holding ZIL tokens, individuals gain access to interact with a wide range of DApps and platform services built on the Zilliqa blockchain. Furthermore, ZIL token holders possess the privilege to participate in network upgrade decisions through staking their ZIL tokens for voting rights.
ZIL tokens total supply is 21 billion tokens. At the time of writing, the supply of ZIL tokens in the market has reached 15,867,699,447.
Use Cases for ZIL
ZIL plays many roles in the Zilliqa ecosystem, acting as the main medium for transactions on the network. In addition, ZIL tokens also serve as a reward to miners for creating new blocks.
Here’s a complete list of how you can use ZIL coin:
| Governance Token | Through the use of Governance ZIL (gZIL) tokens, users enable long-term ZIL holders and network participants to become decision-makers or vote within the network. The supply of gZIL is fixed at a maximum of 722,000 coins. |
|---|---|
| Staking & Earning Rewards | Anyone who buys and stores ZIL can stake ZIL and receive rewards. The minimum stake is 10 ZIL to ensure that no additional gas fees are required to withdraw the rewards earned. |
| Buying and selling NFTs | ZIL allows users to mint, sell and own NFT assets on Zilliqa’s six marketplaces. Users must purchase and hold ZIL tokens in wallets such as Zilpay. |
| Building decentralized applications (DApps | Token holders can create dApps powered by smart contracts that charge transaction fees. In this case, ZIL can act as a gas fee and facilitate transactions, similar to Ethereum. |
| Creating tokens and raising funds | To create a token, you can visit the Savant IDE and enter the token details to launch the token while holding ZIL tokens in your wallet. Additionally, you can raise funds for the token by listing it on the ZILSwap Initial Liquidity Offering (ZILO). There, ZWAP holders (another token on Zilliqa) can provide liquidity to the selected token prior to its launch. |
The Future of Zilliqa
Zilliqa is the first public blockchain to exclusively use a sharded network, allowing it to achieve high bandwidth and transaction throughput, overcoming the scalability issues faced by many blockchains.
Zilliqa is targeting key sectors such as advertising, entertainment, financial services, gaming, and payments. With its advanced capabilities, Zilliqa aims to become the blockchain of choice for large-scale enterprise applications across multiple industries. The technology offers solutions such as data transparency and transaction speed.

On July 5, 2023, Zilliqa implemented a significant upgrade to its main network, reaching version 9.2. This update aimed to optimize network performance and strengthen cross-chain functionality. One of the key improvements was the interoperability between the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Scilla. This enhancement makes it easier to create, test and launch tokens that can be exchanged using ERC-20 and ZRC-2 smart contracts.
How to Buy ZIL Token on PINTU?
You can start investing in ZIL by buying it on PINTU application. Here is how to buy crypto on PINTU app:
- Create a PINTU account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the PINTU balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for ZIL.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you have ZIL as an asset!
Beyond ZIL, you have the ability to invest in alternative cryptographic assets, including BTC, ETH, among others, with relative ease and assured safety. All cryptographic assets included in the PINTU application have undergone a rigorous evaluation, underpinned by a principle of prudence.
PINTU is compatible with popular digital wallets such as Metamask, making transactions more convenient. The application is regulated and supervised by the Indonesian Commodity Futures Trading Regulatory Agency (Bappebti) and the Ministry of Communication and Information Technology (Kominfo).
You can also learn more crypto through the various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
Disclaimer:
This content is intended to expand the reader’s knowledge. Always conduct personal research before investing and use funds that you can afford to lose. All buying and selling activities and investments in crypto assets are entirely the reader’s responsibility.
References
- Bennet Garner, What Is Zilliqa (ZIL)? | The Complete Guide to the High Throughput Blockchain, Coincentral.com, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Cryptowallet.com, ZILLIQA USE CASE, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Sam Lee, What is Zilliqa? $ZIL, Asiacryptotoday.com, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Messari.io, Zilliqa, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Abra.com, What is Zilliqa?, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Sam Klemens, What is Zilliqa (ZIL)?, Exodus.com, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Zenlegdger.io, Zilliqa (ZIL), diakses pada 4 Juli 2023.
- Zilliqa, Upcoming Upgrade of Zilliqa Mainnet to v9.2, blog.zilliqa.com, accessed on 4 July 2023.
- Paschal of Web3, What is (ZIL) and Why is zilliqa blockchain unique?, Medium.com, accessed on 4 July 2023.
Share
Related Article
See Assets in This Article
BTC Price (24 Hours)
Market Capitalization
-
Global Volume (24 Hours)
-
Circulating Supply
-