Understanding Ethereum Virtual Machine

Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is one of the most important parts of the Ethereum ecosystem. Most dApps to NFTs that exist today cannot be separated from the role of EVM. Furthermore, EVM is believed to have a major role in the future development of the crypto and blockchain industry. Find out about EVM and its potential in the following article.
Article Summary
- 💻 The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the software running on the computer of each node participating in the Ethereum protocol.
- 🔍 EVM serves to help developers to develop dApps, write smart contract code, determine the “state” of the Ethereum blockchain, and improve interoperability between blockchains.
- ➕ The advantages of EVM are that it supports interoperability between blockchains, has a high level of security and reliability, and distributed consensus.
- ➖ Currently, the disadvantages of EVM are that it has a low level of scalability, the deployed smart contracts cannot be modified, and there are minimal upgrades from the Ethereum development team.
What is Ethereum Virtual Machine?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the software running on the computer of each node participating in the Ethereum protocol. It serves to execute and run smart contracts that are more often written in a programming language called Solidity on the Ethereum network.
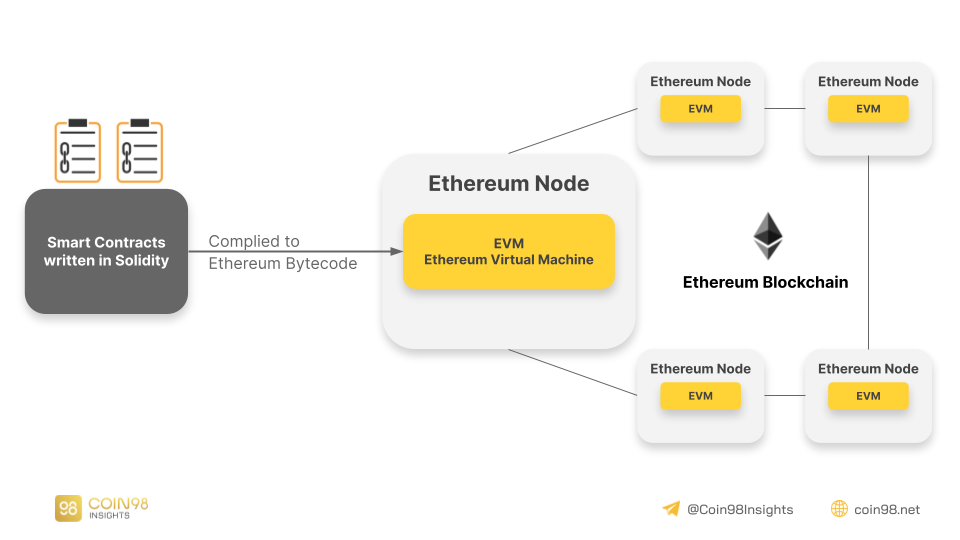
EVMs are Turing Complete, which means they can run a wide range of applications and scenarios. With Turing Complete capabilities, EVMs can process complex calculations, implement decision-making processes, and run various algorithms. This flexibility allows developers to build smart contracts and dApps with ease. The use of EVM also enables smart contracts to benefit from the ecosystem and security features of the Ethereum network.
In addition to helping developers develop dApps and write smart contract code, EVM has many roles in the Ethereum ecosystem. First, it determines the “state” of the Ethereum blockchain when new blocks are added. Secondly, EVM also improves interoperability between networks.
Interoperability is the ability to communicate, share data, and interact between different blockchain networks smoothly and efficiently.
Through EVM, all dApps built on it become compatible with each other. Users can also bridge tokens and migrate between EVM-compatible blockchains. These blockchains can interact with the EVM network efficiently and securely with improved interoperability.
You can learn more about Layer-2 Ethereum and its scalability solutions in the following article.
How Does Ethereum Virtual Machine Work?
EVM uses a “stack” based computing model, which means the nodes come in a particular order. Having a strict pre-defined order helps Ethereum resist hacker attacks and increase efficiency. As mentioned, various programming languages can be used in EVMs, but EVMs cannot read these coding languages. Therefore, compilers will convert the coding language into EVM-readable code, i.e., bytecode.
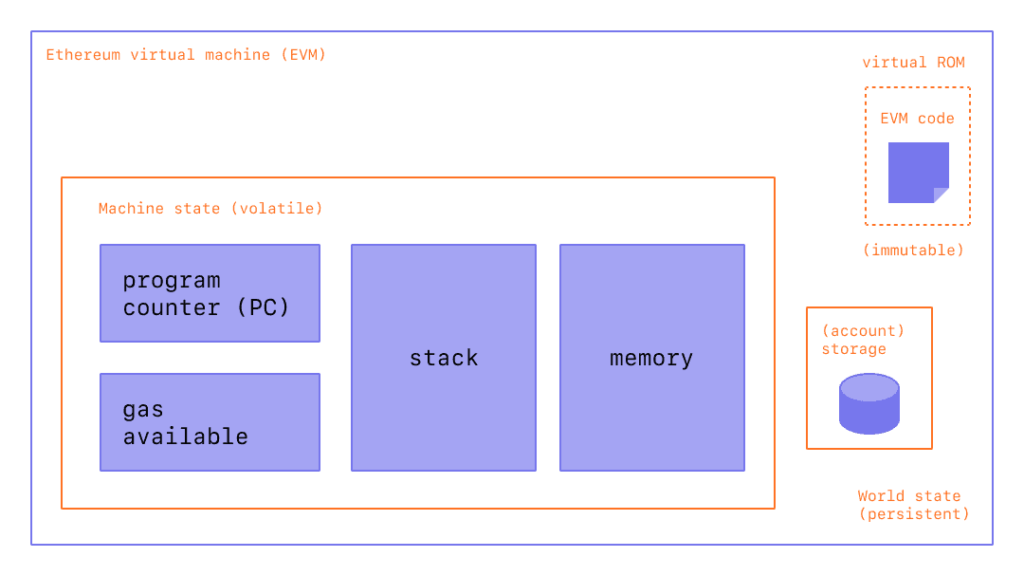
Afterward, each bytecode will be processed by EVM and distributed to all nodes on the Ethereum network. At the same time, EVM will also interpret the bytecode into the form of Opcodes to be able to execute all existing instructions from the smart contract.
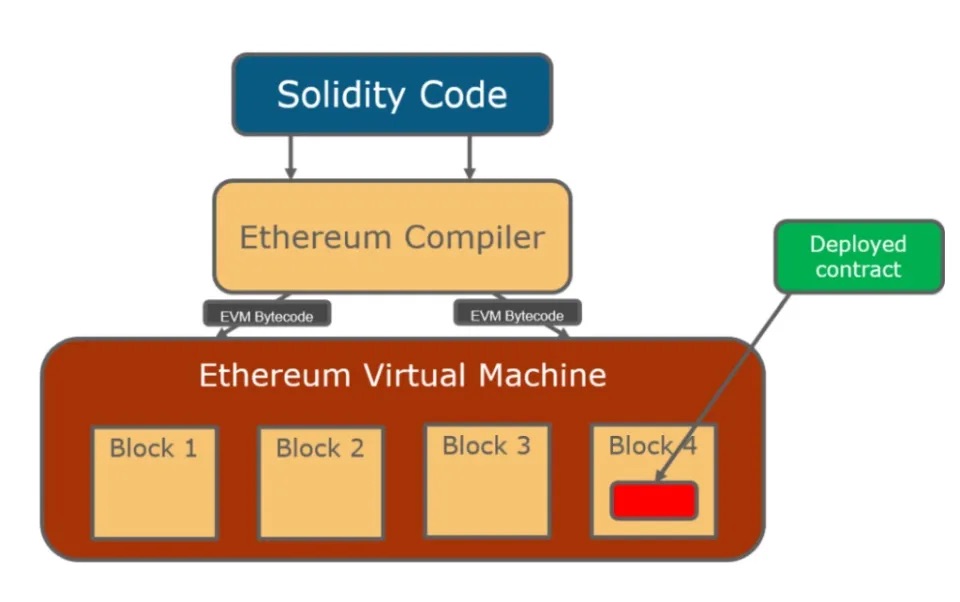
Each operation has a particular cost, measured in units of “gas.” The gas price will be determined by the complexity level and the resources required to run the smart contract. The more complex and extensive the resources required, the more expensive the gas fee will be. This gas fee is then paid by users in ETH.
The Benefits of Ethereum Virtual Machine
The following are some of the advantages offered by EVM:
- Supports interoperability between blockchains. EVM can support all types of blockchains that use bytecode-based smart contracts. EVM also allows developers to connect with various layer-2 networks. This makes it easy for asset bridging or migrating dApps between blockchains.
- Security and reliability. EVM creates a decentralized and isolated environment for running smart contracts. This ensures that data will remain safe and can run smoothly. In addition, EVMs have proven security.
- Distributed consensus. EVM executes smart contracts through distributed consensus. This ensures that when a node fails, it will not affect the DApps or smart contracts in operation.
Also, read the following articles about the current state of Ethereum after The Merge update
The Drawbacks of Ethereum Virtual Machine
With the various advantages EVM offers, it unfortunately still has some drawbacks.
- Scalability. Currently, the level of scalability of the Ethereum network and Ethereum’s layer-2 is lower compared to centralized networks. Ethereum 2.0 is an attempt to fix these scalability issues.
- Smart contracts are immutable. The development team will be inconvenienced when a bug or other problem is found in the smart contract. Inevitably, the development team will have to relaunch the smart contract, which means additional costs will be required.
- No significant updates. Since its launch in 2015, EVM has yet to undergo any substantial updates. The Ethereum development team has focused updates on other aspects of Ethereum.
The Future of Ethereum Virtual Machine
The future of the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) looks promising, especially with increasing adoption rates, the ongoing development of the cryptocurrency sector, and Ethereum’s continuous breakthroughs. Additionally, cross-chain interoperability has become a major focus in the crypto industry. The EVM plays a crucial role in enabling this interoperability by acting as a bridge between Ethereum and other blockchains. Furthermore, there are now several EVM-compatible blockchains, including Polkadot and Cosmos, further expanding the possibilities for seamless interaction across different networks.
Most recently, zkSync has also introduced EVM-compatible zero-knowledge rollup (ZK-rollup) technology called zkEVM. Through zkEVM, developers can write ZK-based smart contracts (previously using the complicated R1CS) using Ethereum programming languages such as Solidity. In addition, Ethereum DApps developers also migrate to the ZK-rollup network that uses zkEVM.
Pintu Academy has prepared a full review of the technology and how zkSync works in the following article.
EVM can also play a role in facilitating the exchange of assets and tokens between blockchains through the atomic swap mechanism. This lets users move their assets between different blockchain networks quickly and securely. Thus, creating a more liquid and inclusive market.
One of the most anticipated developments is the planned update of the EVM Object Format (EOF) in 2023. EOF will be the first update to EVM since its inception in 2015. In short, this update will change how EVM works, enabling cheaper and faster smart contract creation. In terms of security aspects, EVM will also experience improvements.
Conclusion
EVM is the backbone of the entire Ethereum network ecosystem that exists today. Despite the emergence of blockchains that have the “Ethereum killer” status, Ethereum and its EVM are still the first choice for development teams to create dApps. However, scalability issues and high gas fees are still a big chore for EVM.
Fortunately, the Ethereum team is not standing still. Through the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade plan, scalability solutions via layer-2, and the development of cross-chain interoperability, EVM will still have an important role in the growth and transformation of the crypto and blockchain industry going forward.
Buy Crypto Assets in Pintu
Interested in investing in crypto assets? Take it easy, you can buy various crypto assets such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily. Furthermore, Pintu has subjected all its crypto assets to a thorough evaluation process, emphasizing the importance of prudence.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to executing transactions, in the Pintu Apps, you can also learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles updated weekly! All Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice.
References
Ethereum Team, Ethereum Virtual Machine, accessed on 10 May 2023.
Ethereum Team, Layer-2 Scaling, accessed on 10 May 2023.
Max Hinchman, Ethereum Virtual Machine, Messari, accessed on 11 May 2023.
Lipsa Das, Understanding Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), Ledger, accessed on 11 May 2023.
Coin Telegraph, What is blockchain interoperability: A beginner’s guide to cross-chain technology, accessed on 11 May 2023.
Simran Jagdev, Cross-chain Interoperability Is the Future of DeFi, Consensys, accessed on 11 May 2023.
Federico Kullmer, Where Is the Ethereum Virtual Machine Headed in 2023? CoinDesk, accessed on 11 May 2023.
Share