What is Modular Blockchain?
Scalability is still a significant issue for blockchain to reach mass adoption. The monolithic blockchain structure is the reason behind the low level of scalability. Now, modular blockchains are starting to be developed as one of the solutions to overcome these scalability issues. What is modular blockchain? And how can it be a solution? Check out the full review in the following article.
Article Summary
- ⛓️ A modular blockchain is a blockchain that separates tasks into specific layers, unlike monolithic blockchains that run everything in one layer.
- ♻️ Modular blockchain is a solution to address the blockchain trilemma, which is the challenge of balancing scalability, security, and decentralization.
- 👍 The main advantages of modular blockchain include better scalability, flexibility for development teams, and efficiency in transaction processing.
- 🚨 Modular blockchain also comes with some challenges such as high complexity and potential security risks.
- 🎯 With the increasing need for scalability and flexibility, modular blockchain has the potential to become the foundation of blockchain technology in the future.
What is Modular Blockchain?
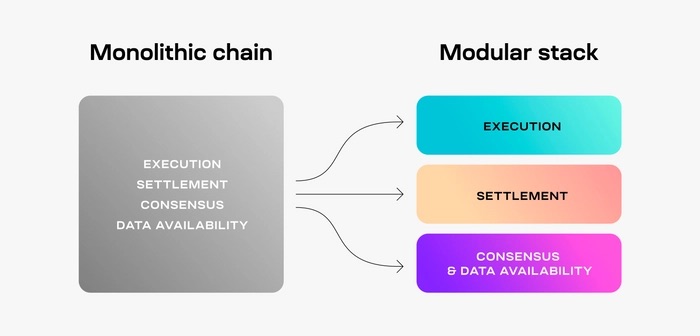
Before we talk about modular blockchains, let’s recall the layer structure of a blockchain: execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability. Typically, blockchains run their task on these layers as a unity, otherwise known as monolithic blockchains.
Recently, modular blockchains have emerged as an alternative way of creating blockchains. Instead of executing all tasks as a single entity, modular blockchains separate those layers and perform their tasks separately according to their respective specializations.
Learn more about the blockchain trilemma problem and its full explanation in this article.
To make it easier, let’s first understand the “tasks” of each layer:
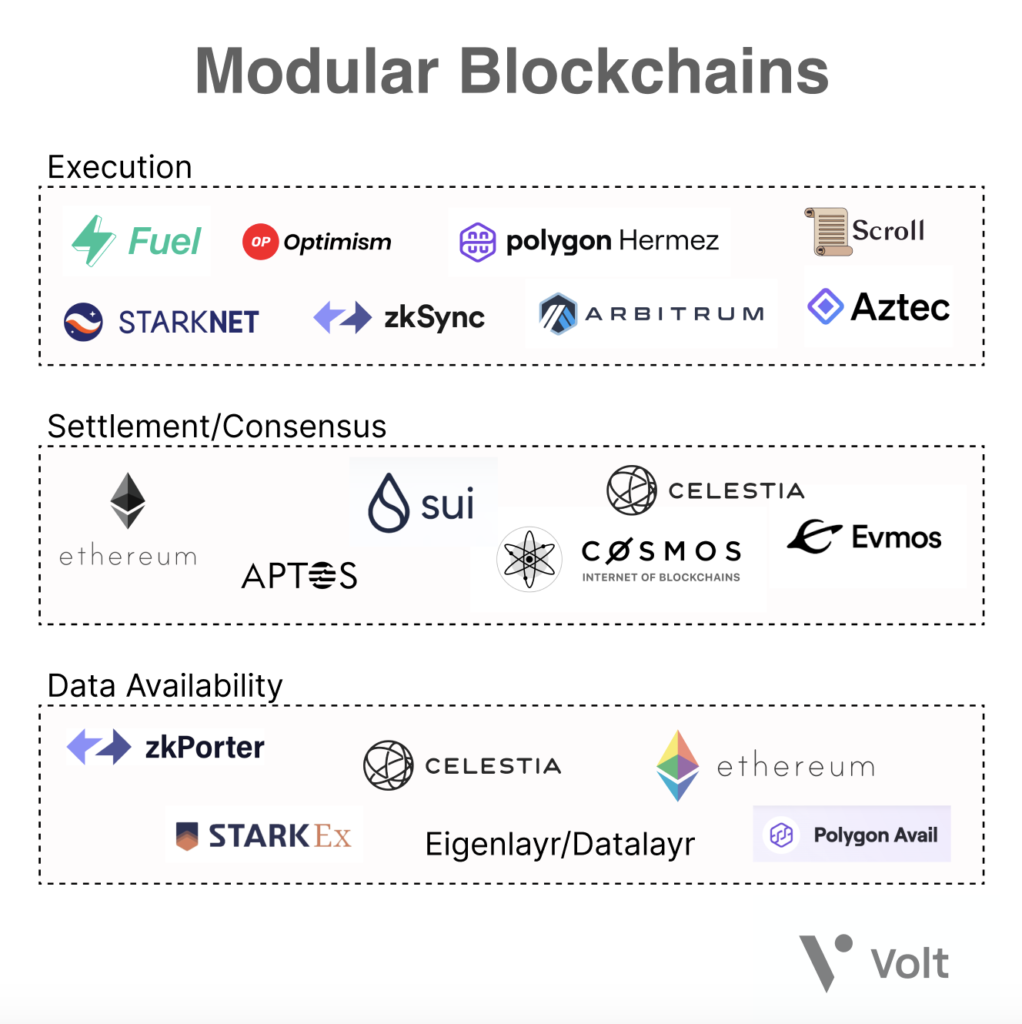
- Execution. The layer where transactions are executed, as well as the deployment and interaction with smart contracts.
- Consensus. The layer where the contents and ordering of a transaction are agreed upon.
- Settlement. The layer where transactions are settled, settling disputes, validating proofs, and bridging between different execution layers.
- Data Availability. The layer that stores and ensures the availability of data to be used as a reference for all transactions.
Blockchains can be more effective by separating functions where each layer does a specific task. So, the block space generated will be larger and the validator’s job will be lighter. Ultimately, this can improve the transaction processing of a blockchain.
How Modular Blockchain Works
Several issues arise as more Dapps are built on top of monolithic blockchains. These range from limited flexibility for developers’ teams to network congestions that drive up costs. Modular blockchain design is an attempt to overcome these problems.
As the name implies, modular blockchain works on the principle of modularity. Simply put, it separates a system into parts that can subsequently be combined, modified, and interchanged to fulfill certain needs. Modularity relies on specialization where each component can only do a few things but must be done well.
In a way, modular components are similar to Legos that can be combined to form various structures. Each component is an interchangeable module that can be replaced or connected.
The architecture of a modular blockchain is a three-layer structure that runs independently. The development team can modify, upgrade, and replace each layer, making the blockchain more flexible. Since each layer has its specialization, its performance becomes more optimized. This can increase scalability, reduce gas costs, and create faster performance.
Difference Between Monolithic and Modular Blockchain

As explained earlier, the main difference between modular and monolithic blockchains lies in the structure of the layers and how each accomplishes its tasks. With a monolithic architecture, the performance of the blockchain will be very limited as nodes have to do everything. In a modular architecture, each layer is separated, and each node has a specific task, optimizing its performance while allowing for more use cases.
Main differences between monolithic and modular blockchain:
| Feature | Monolithic Blockchain | Modular Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | All tasks run simultaneously on one layer | The layer structure is separated depending on each task |
| Specialty | Generalist | Specialist |
| Flexibility | The dApps developers team must follow the existing structure | The dApps team can customize the structure depending on their needs |
| Scalability | The scalability is more limited because all tasks are done in a single entity | Each layer performs its own tasks, so many components can be modified to improve scalability. |
| Security | Has a better security level | If the security layer isn’t effective, the security risk is higher |
| Complexity | Much simpler | More complex |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Modular Blockchain
Advantages of Modular Blockchain
- ⚡ Scalability. Monolithic blockchain has an inherent scalability problem as all activities are performed simultaneously on a single layer. Modular blockchains can improve scalability by modifying or changing components that need updates.
- 🧩 Flexibility. Modular blockchains give the development team complete control when creating applications. They can develop mechanisms, rules, and so on according to their needs and principles. Unlike monolithic blockchains, where every mechanism and rule is predefined.
- 🤝 Shared Security. Modular blockchains no longer require the development team to create consensus mechanisms and validators from scratch. They can choose to get both from other networks in the same ecosystem. Having the same security aspects can help create secure bridges between chains. An example is modular Layer-2 networks.
The modular concept is also applied to layer-3 networks. Learn more in the following article.
Disadvantages of Modular Blockchain
- 🌀 Complexity. Modular blockchains have a more complex architectural design. For example, the execution layer must have mechanisms such as fraud and validity proofs to allow the security layer to enforce the validity state of transitions. Modular blockchains must also consider composability for applications built on top of them.
- 🔐 Security. Modular blockchains cannot guarantee the quality of their security level. If the security layer (generally controlling consensus and data availability) isn’t safe, then modular blockchains are at risk of failing.
- 🪙 Value Token. Some modular blockchains will struggle to create value in their native tokens as they are underutilized. For example, if the focus layer is for consensus and data availability, the utility token will have a lower value than the utility token on the execution layer.
Examples of Modular Blockchains
1. Layer 2 Ethereum
One way to increase scalability on a blockchain is to use rollups. Ethereum’s Layer 2 (L2) networks, such as Arbitrum and Optimism, use this technology. Actually, the mechanism and concept of rollup make it similar to modular blockchains.
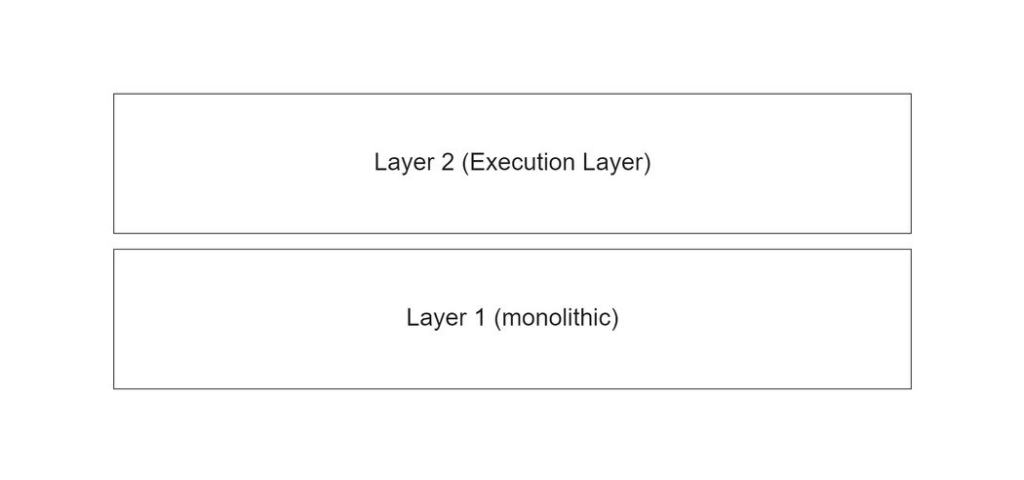
Rollup as L2 works by separating the execution layer from the main network (Ethereum). Ethereum as L1 continues to carry out settlement, consensus, and data availability functions. Rollups optimize the execution layer by having faster block times and cheaper gas fees but without sacrificing Ethereum’s security and decentralization aspects.
However, the rollup scalability solution still leaves one major problem: dependence on Ethereum’s data availability layer. So, when the Ethereum network is congested, the gas price on the L2 network will also increase. In addition, the development team cannot create DApps that EVM does not support.
Find out more about L2 and how their technology works in this article.
2. Celestia
Celestia is the first modular blockchain network. It offers a low-cost and easy process of creating blockchains and dApps by providing a consensus layer and data availability. Unlike Ethereum, Celestia is completely modular, allowing developers to modify their dApps as needed.
Celestia uses roll-up technology to enable all this. Celestia is like a house that receives rollups from various dApps. After that, Celestia processes all transactions and ensures data availability for all dApps.
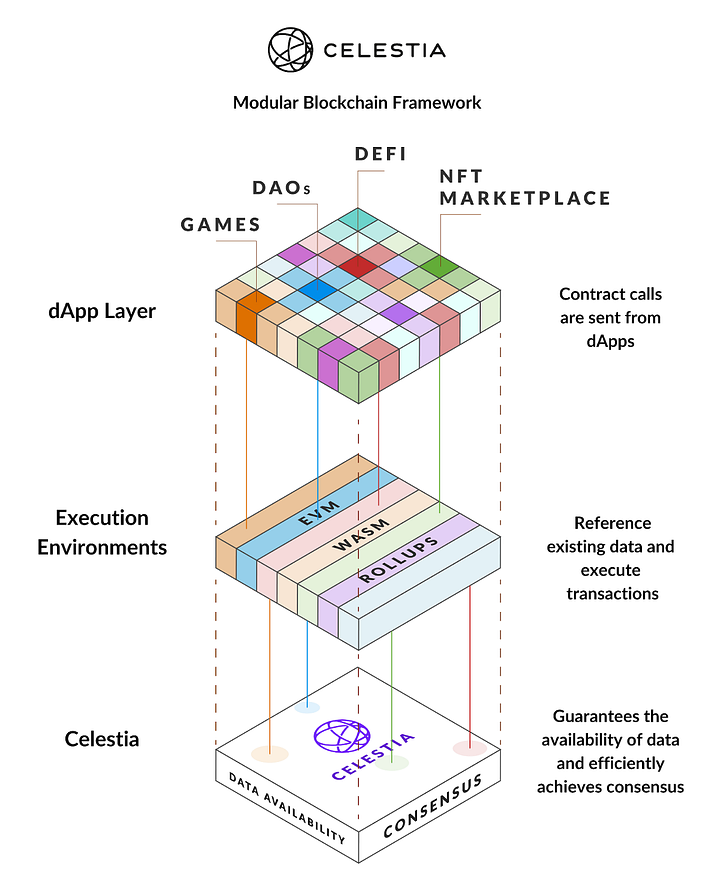
With modular blockchain, Celestia also wants to create a collaborative ecosystem with many interconnected chains. By becoming a home for Dapps from various rollups, they no longer need to fight for computing resources with each other. Everything will be shared and connected through Celestia.
The Future of Modular Blockchain
Currently, the blockchain industry is still facing scalability issues. One of the reasons is the use of monolithic blockchains that keep all transaction processing in one place. Relying on monolithic blockchains in the long run only magnifies the problem.
Mass adoption of crypto and blockchain means more transactions must be processed. On a monolithic blockchain, this will cause enormous amounts of data that need to be processed. The network architecture of monolithic blockchains is not ideal for processing such a large number of transactions in a short period.
Therefore, modular blockchain is considered to be one of the solutions to overcome these problems. Modular blockchain and roll-up technology will break down these tasks according to their structures, making the process more optimized and practical.
Celestia Labs Chief Operating Officer Nick White said that, like a collection of building blocks, the modular blockchain will connect to the availability data layer as part of a unified ecosystem. So, nodes don’t need to download all transactions like on a monolithic blockchain.
According to him, rollups can allow nodes to verify transactions by downloading less than 1% of the size of a block. As a result, the entire process can be done using only a smartphone.
How to Buy Cryptocurrency on Pintu
Looking to invest in crypto assets? No worries, you can safely and conveniently purchase a wide range of cryptocurrencies such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily on Pintu. Pintu diligently evaluates all its crypto assets, highlighting the significance of being cautious.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
Aside from buying and trading crypto assets, you can expand your knowledge about cryptocurrencies through various Pintu Academy articles. Updated weekly, all Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice
References
- Stephanie Dunbar, The Modular Blockchain Landscape, Messari, accessed on 15 September 2023.
- Darren Kleine, The Future Is Light: Blockchain Goes Modular, Blockworks, accessed on 15 September 2023.
- Alec Chen, Modular Blockchains: A Deep Dive, Volt Capital, accessed on 15 September 2023.
- Celestia Docs, Modular and monolithic blockchains, accessed on 15 September 2023.
Share