What is Layer 3 Crypto?

The layer 2 ecosystem is currently dominating the crypto industry thanks to its scalability solutions. By implementing Layer 2 solutions, transactions on the Ethereum network have become faster and more cost-effective. However, discussions and initiatives surrounding Layer 3 have also started to surface, representing a potential new breakthrough with even higher scalability than Layer 2. So, what exactly is layer 3? How far has it progressed? Read the full story in the following article.
Article Summary
- ⛓️ Layer 3 is an additional layer built on top of a blockchain network’s Layer 2 Ethereum to provide additional scalability and customization. This makes it a layer that can be specialized according to the needs of each development team.
- ⚡ The advantages that layer 3 offers are better scalability and choosing specific scalability solutions (such as privacy). It also gives flexibility to the developer to change each chain according to their needs.
- ⚙️ Some layer 3 projects currently in development are Arbitrum’s Orbit and ZK Stack’s Hyperchain. In addition, StarkWare is also preparing its layer 3 project.
What is a Layer 3?
The term layer 3 is actually debatable and has different definitions. However, it is generally defined as a blockchain built on top of a layer 2 network. So far, layer 3 itself is still in its early stage phase.
If layer 2 was created to increase scalability and solve the problems that exist in layer 1, it is the same as layer 3. It is a solution to overcome the problems that layer 2 currently faces. So far, layer 3 technology can only be developed and applied to the Ethereum network.
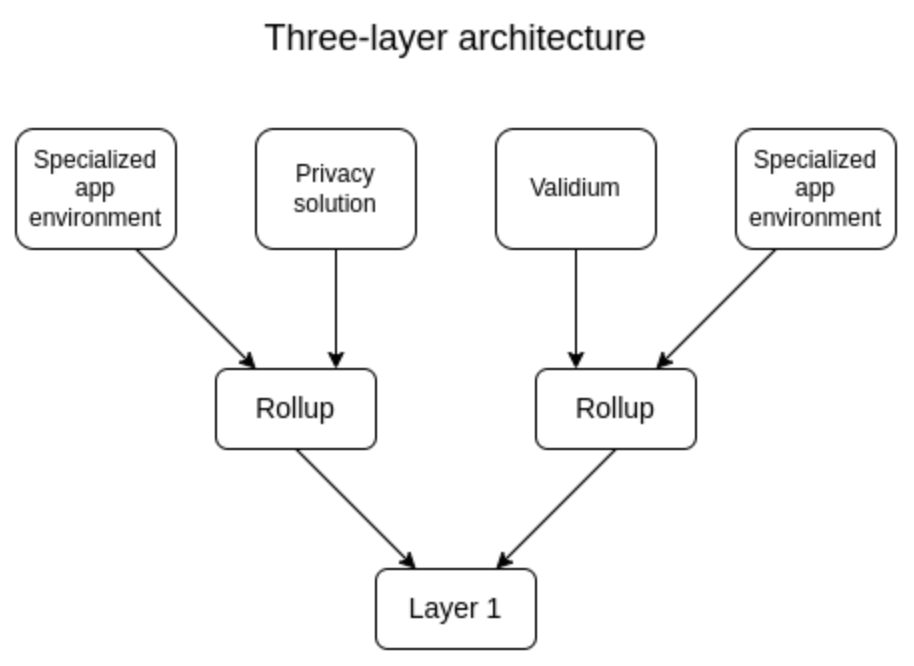
Currently, the layer 2 network acts as a scalability solution that accommodates general purposes. While layer 3 offers a specific scalability solution and a network that can be customized based on needs. This makes it a suitable technology for dApps that require a high level of customizability.
Many people think layer 3 is similar to the appchains network, like in Cosmos. It is because they can both be customized and optimized for specific needs. However, they are two different things. Appchains are defined as a single blockchain created specifically to accommodate the creation and operation of decentralized applications (dApps). It is separate yet connected to the main blockchain.
In short, layer 3 is a network where the development team can customize the system according to their needs. Applications built on layer 3 networks will have faster transaction processing than layer 2. However, they still have the same level of security and decentralization as layer 2.
How Layer 3 Works
The way layer 3 actually works cannot be as simple as creating a new network on top of a layer 2 network. Vitalik Buterin, in his essay on layer 3, mentions that there are limitations in “stacking” new networks on top of existing networks. This might work for a layer 2 network built on top of a layer 1 network, but it won’t work for a layer 3 network built on top of a layer 2 network.
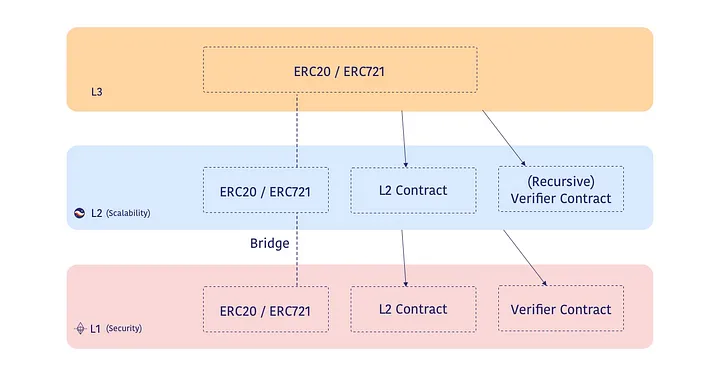
In rollup technology, for example. It uses a compression technology where various data is collected and “rolled” into one. Unfortunately, the compressed data cannot be compressed and rolled up again. Therefore, rollups on top of rollups are not possible.
However, building a network on top of layer 2 with specific purposes and specializations is possible. By using layer 2’s network as a base, layer 3 does not need to build its own validator system. It can use layer 2’s validator network and inherit the security aspects of the protocol, whether rollup or zero-knowledge.
This is exactly what Starkware, one of the companies focused on developing layer 3 solutions, is doing. The chart below shows that there are networks in layer 3 that each serve a specific purpose.
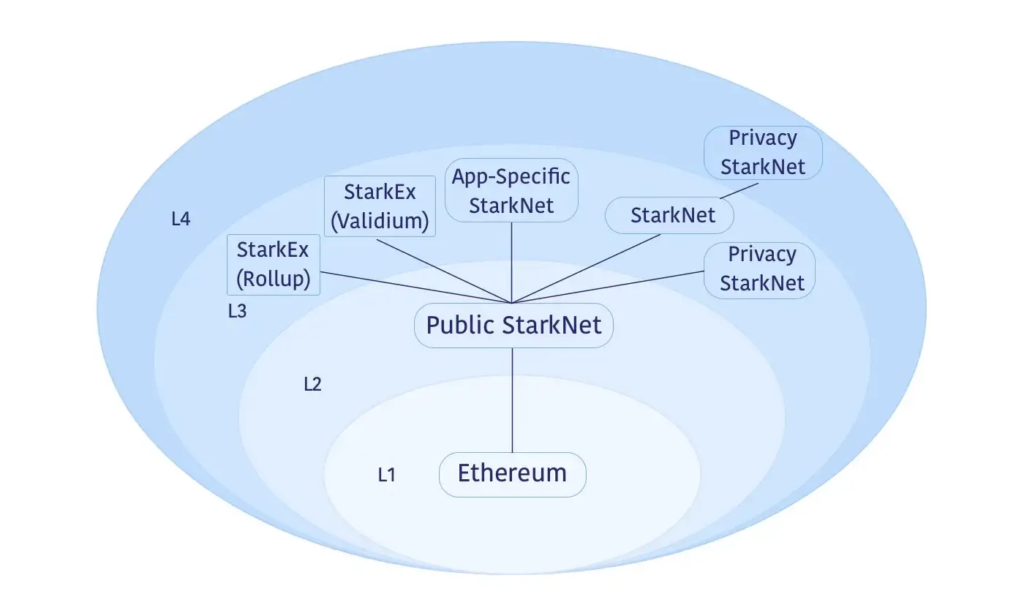
So, layer 2 is used as a general-purpose scaling solution, but layer 3 has specific functionality. Layer 3 can have functions that are specialized for privacy, specific application performance, or other purposes according to the development team’s needs. Besides Starkware, Arbitrum through Arbitrum Orbit, also develops layer 3 with the same concept.
Advantages of Layer 3
- ⚡ Scalability. With multiple chains that are each dedicated and have separate resources, it is easier to overcome layer 2’s bottleneck problem.
- 🎯 Specific. If layer 2 is used as a general scalability solution, layer 3 will have specific scalability solutions. For example, a privacy-focused scalability function solution. This is possible because layer 3 can increase an application’s computing speed and scalability without sharing the chain with other applications.
- ⚙️ Flexibility. Each chain in layer 3 will be customizable according to the needs of each development team. Starting from sequencer selection to data availability mode. This provides flexibility for the development team instead of using chains with predefined mechanisms like in layer 2.
Some Layer 3 Projects
1. Arbitrum Orbit
Arbitrum Orbit is a part of Arbitrum that allows developers to easily and permissionless launch their own layer 3 ecosystem. The Arbitrum Orbit chain can be built on Arbitrum’s layer 2 network, Arbitrum One or Arbitrum Nova.
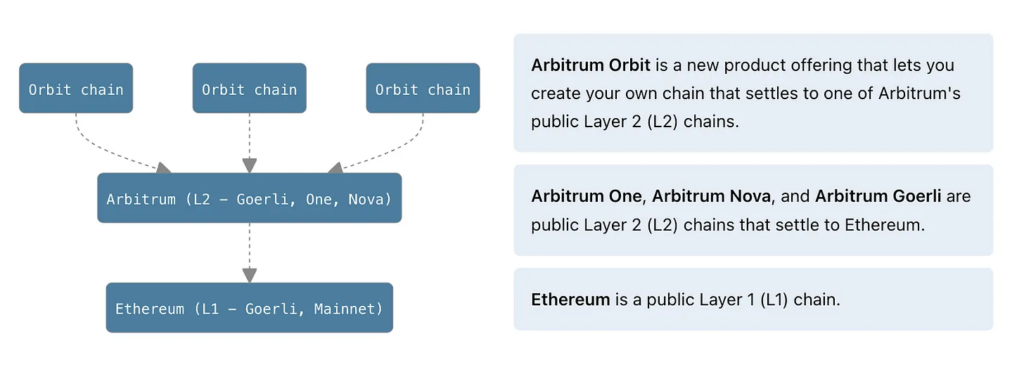
If you choose Arbitrum One, which uses the rollup protocol, its layer 3 characteristics will prioritize security but still have good scalability. Meanwhile, if you select Nova Arbitrum, which uses the anytrust protocol, then its layer 3 will focus on the level of scalability but sacrifice the level of security.
As mentioned, layer 3 has the characteristic of being customizable to the needs of the developers. Arbitrum Orbit also offers chains that can be designed according to specific needs.
Arbitrum Orbit also allows users to create AnyTrust or Rollup chains using their existing infrastructure. Think of it like a self-managed priority line on Ethereum. So, Arbitrum Orbit has the support capacity of Ethereum while still getting the security aspects of Ethereum.
To accommodate further network modifications, Arbitrum will soon launch Stylus. The update allows the developers to use non-EVM programming languages such as C++ and Rust.
2. ZK Stack
Another company that is developing the layer 3 concept is Matter Labs through ZK Stack. The project is a modular framework for creating an independent Zero Knowledge-based Hyperchain (layer 3). ZK Stack is based on the open-source code of the zkSync Era layer 2 network.
In the future, the ZK Stack will give the developers complete freedom to choose the data availability mode from native tokens or decentralized sequencers. The hyperchain will operate independently and rely on Ethereum for its security aspects. It will be supported by Hyperbridges that connect between Hyperchains. Thus, creating an ecosystem that is trustless, fast, and has low transaction fees.
Some projects that are claimed to be suitable for using ZK Stack’s Hyperchain are listed below:
- dApps that require lightweight sequencers with a low latency of sequencing
- Apps that can interact without the trust assumptions of bridges
- A closed private chain with connectivity to the ecosystem
- A way to use a native token as your system’s base token
In terms of security aspects, ZK Stack will adopt zkSync Era’s ZK rollup technology that has been tested on the Ethereum network. In the end, ZK Stack’s layer 3 will not only offer an independent network that can be customized. But it will also inherit the security aspects of Ethereum’s layer 1.
Layer 3’s Potential in the Future
It’s too early to imagine what impact layer 3 will have on the crypto ecosystem. After all, Ethereum layer 2s like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync are just starting to dominate the crypto ecosystem.
Layer 3 also faces several challenges that must be resolved before full implementation.
- 🔐 Security. So far, the mechanism of how validators work in layer 3 follows the technology used in layer 2. This means that exploring and developing rollups and ZK technology is vital to ensure the development of the security aspects of layer 3 itself.
- 🌐 Interoperability. To ensure interoperability between layer 3 networks, there is still a need for a clearer pattern and structure of mechanisms. So far, the layer 3 developers still need to find interoperability solutions between these networks.
- ⚠️ Complexity: Layer 3 protocols are complex, and layer 2 itself is still evolving. The development team must ensure that layer 3 flexibility can keep up with the dynamic development of layer 2.
Layer 3 technology is anticipated to be a long-awaited breakthrough, offering enhanced and more targeted scalability while providing developers with greater flexibility. This makes it the ideal choice for developers seeking to create applications with specific functions.
On the other hand, the existence of layer 3 will not affect the popularity of layer 2. This is because all transactions in layer 3 will also use the layer 2 ecosystem. Thus, the adoption of layer 3 projects will benefit layer 2 because they get transaction fees. In the future, as the layer 2 and layer 3 ecosystems continue to grow, Ethereum, as a layer 1 network, will reap the advantages.
Buy Crypto Assets in Pintu
Looking to invest in crypto assets? No worries, you can safely and conveniently purchase a wide range of cryptocurrencies such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily at Pintu. Pintu diligently evaluates all its crypto assets, highlighting the significance of being cautious.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
Aside from buying and trading crypto assets, you can expand your knowledge about cryptocurrencies through various Pintu Academy articles. Updated weekly, all Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice.
Reference
- Tony Kreng, What is a Layer 3 Crypto? Data Wallet, accessed on 27 July 2023.
- Vitalik Buterin, What kind of layer 3s make sense? accessed on 27 July 2023.
- Foresight Ventures, Layer 3 in-depth, Medium, accessed on 27 July 2023.
- Gidi Kaempfer, Fractal Scaling: From L2 to L3, StarkWare, accessed on 27 July 2023.
- Arbitrum Docs, A gentle introduction: Orbit chains, accessed on 27 July 2023.
- Zk Sync, Introducing the ZK Stack, Matter Labs Medium, accessed on 27 July 2023.
- The Defi Investor, L3s are coming to Ethereum, Twitter, accessed on 27 July 2023.
Share