What is Polygon (MATIC)?
Polygon Network (MATIC) is a decentralized protocol for building and connecting multiple Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Polygon provides solutions to several blockchain-related scalability issues, such as high gas fees and slow speeds, but without compromising security.
MATIC is Polygon’s native ERC-20 token for paying transaction fees and a governance token. In addition, you can use MATIC for staking.
Currently, there are around 4.8 billion MATIC Tokens circulating in the market. The maximum supply of MATIC is 10 billion and Polygon adds new tokens every month. According to the release schedule, all MATIC tokens will be on the market in December 2022.
The history of Polygon
Polygon was originally called Matic Network, created in 2017. Matic was created by several Ethereum developers, namely Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun, and Mihailo Bjelic. They created Matic because they saw Ethereum’s scalability issues where increasing network density leads to high gas fees and slow transaction processing. Matic provides layer 2 scalability solution to that problem.
During its initial offering in April 2019, the team raised $5.6 million in ETH through the sale of 1.9 billion MATIC tokens over a 20 day period. Then, Matic Network launched in 2020 and Matic changed its name to Polygon Network in February 2021.
This name change corresponds to Polygon’s shift in strategy from simply providing layer 2 for the Ethereum network to creating an entire blockchain networks infrastructure for other developers. Now, Polygon hopes to provide a blueprint for various layer 2 solutions and create a multi-blockchain that can work in tandem with the Ethereum network.
How Polygon works
Polygon is often referred as “Ethereum’s Internet of blockchain” because it creates a multi-chain ecosystem interoperable with Ethereum. It was created as a layer 2 solution to the frequent overcrowding on the Ethereum network. This is especially troublesome for DeFi (decentralized finance) and DApps (decentralized applications) developers because their users has to spend more gas on their applications.
Then, what is layer 1 and 2? Layer 1 (L1) is a term for describing mainnet Ethereum as the main blockchain network while layer 2 (L2) is the blockchain that runs alongside it. Layer 2 solutions solve Ethereum’s scalability problem by processing Ethereum transactions on the Polygon networks. This is so that users do not suffer losses due to the density of the Ethereum network.
Read more: What is Ethereum and how does it work?
Polygon provides several layer 2 solutions for developers, two of those are commit chains and side chains (blockchain that runs parallel alongside mainnet Ethereum). The main difference between the two systems is that commit chains can internalize the security of the Ethereum network. This allows developers to take advantage of Polygon’s scalability but still enjoy the security provided by the Ethereum network.
So, Polygon provides technology to improve blockchain performance, allowing faster transactions and cheaper gas fees than mainnet Ethereum. Additionally, Polygon also aims to provide frameworks for developers to create a blockchain network compatible with Ethereum. Effectively incentivizing them to migrate their applications to Polygon.
This makes Polygon invaluable for small-to-medium-sized enterprises and developers concerned with Ethereum’s network congestion. As a long-term scalability solution, Polygon has the potential to provide a wide range of utilities for developers. This potential creates a unique value proposition for the MATIC token.
The Polygon ecosystem
Many developers are starting to see the potentials of Polygon. Apps like Aavegotchi said that migrating from the Ethereum mainnet to save their users hundreds of thousands of dollars that would normally be spent on gas fees on Ethereum. Now, Polygon offers various DApps on its network including some you can use for profits.
Some of the DApps in Polygon:
- Quickswap
Quickswap is a DEX (decentralized exchange) on the Polygon network that allows users to make fast transactions with low gas fees. It is initially created as a fork or modification of the Uniswap protocol. QUICK is the native token of Quickswap and is quickly becoming the most active Polygon project by user count, with over 225,000 users over the last 30 days (August 2021).
Furthermore, the trading volume in Quickswap exceeds more than $4.5 billion. You can use Quickswap to exchange various types of cryptocurrencies with low transaction fees or deposit your assets and become a liquidity provider on the network.
- Aavegotchi

Aavegotchi is a blockchain-based game that combines elements from both DeFi and NFT. In it, you will buy (spawn) and collect NFT in the form of avatars backed by cryptocurrencies. So, every gotchi you have is an asset whose value depends on the cryptocurrencies you store in the gotchi when you spawn it.
$GHST is the native token of the world of Aavegotchi which you can use for various interactions including buying in-game items and staking.
The characteristics of each gotchi can be continuously improved in the game. The more experience you have, the more valuable your gotchi will be. Buying clothes, playing minigames, and doing other interactions also increase the value of the gotchi. The higher the level and rarity of your gotchi, the higher the profit you can get in-game. The thing you need to pay attention to before playing Aavegotchi is that you need to lock and store your crypto assets as collateral attached to your gotchi.
- KogeFarm
KogeFarm is a DeFi yield farming application, which is a way to earn passive income. In simpler terms, yield farming means locking or storing crypto assets in DApps and earn interest within a certain period of time. In the context of conventional banks, yield farming is very similar to time deposit.
KogeFarm is unique in that it is one of the DeFi that gives interest both the asset that you save (saving ETH will get ETH) and also KogeCoin tokens. KogeFarm became popular because it took a small profit from its users’ yield, which was 0–1%. It is important that you must consider the risk of yield farming because the wrong strategy can cause permanent losses.
What can you do with the MATIC token?
1. Long-term investment
The MATIC token has experienced a rapid increase since the beginning of 2021, related to the change in name of the MATIC network to Polygon. Similar to cryptocurrencies in general, the MATIC token suffers from high volatility in the short and medium term.
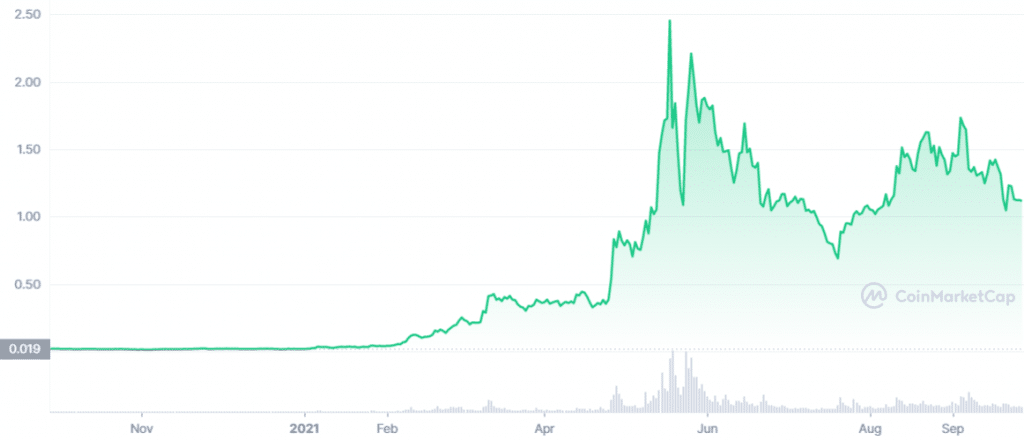
Polygon is still in the developmental phase. Even so, there are already more than 350 applications running on its network. These include popular DeFi projects such as Aave and SushiSwap which are starting to include Polygon network in their services. In addition, native Polygon applications such as Quickswap are also gaining popularity.
However, as an Ethereum protocol, Polygon is heavily influenced by the policies, regulations, and performance of Ethereum. In addition, you need to watch two main competitors who also offer the same scalability solutions, Polkadot and Avalanche, which currently (September 2021) have a higher market capitalization.
So, you need to consider two important things before investing in Polygon. On one hand, Polygon has great potential because its scalability framework is still developing and DApps in its network continue to grow. On the other, you need to pay attention to the launch of Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2) and the activity of Polygon competitors like Avalanche and Polkadot.
2. Staking your MATIC token
The Polygon network uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which is a security system that uses validators and delegators. Validator verifies new transactions and adds them to the blockchain. They may receive a newly created MATIC. Validators must be running the node (or computer) full time and stake their MATIC. Delegators stake their MATIC indirectly through trusted validators.
Please note that if your chosen validator makes a fatal error, you may lose some or all of your staked MATIC.
You can use your MATIC token to be a delegator or stake it directly on the network. Staking is an investment strategy to get passive income with relatively low risk. The MATIC token is one of the many crypto assets you can use for staking.
How to buy MATIC coin?
You can start investing in MATIC tokens in the Pintu app. Through Pintu, you can buy MATIC and other crypto assets in an all in one convenient application.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download the Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bapeppti and Kominfo.
Sources:
- What is Polygon Matic – Coinmarketcap
- What is Polygon Matic and why it matters – Decrypt
- A deep dive into the Polygon Matic ecosystem – The TIE research
- Polygon (MATIC): The Swiss Army Knife of Ethereum Scaling – Gemini
- Should you (or anyone) buy Polygon? – The Ascent
- Polygon homepage
- Analyzing Polygon’s proof-of-stake network – Consensys
Share