What is Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?

Along with the development of technology, trading crypto assets is no longer dependent on intermediaries or third parties. This transformative shift is realized through decentralized exchange (DEX). DEXs enable transactions to transpire directly between users, free from the involvement of intermediaries. In addition, DEX also offers transactions that are transparent and decentralized. DEX is an actual embodiment of the crypto asset concept that promotes decentralization with peer-to-peer transactions. In this article, we will take a closer look at what DEX is and how it operates decentralized.
Article Summary
- ✨ DEX is a peer-to-peer crypto asset exchange platform where users can trade crypto assets without third-party intermediaries. DEX operates on the blockchain and uses smart contracts for automatic transaction settlement.
- 🎉 Users can exchange crypto assets directly through crypto wallets interacting with DEX smart contracts, giving them full control over their assets.
- ✌️ There are two types of DEXs available today: DEXs with an order book mechanism and Automated Market Makers (AMMs). AMMs are the most widely used DEX mechanism.
- 😎 DEXs have advantages such as full asset control, transparency, privacy convenience, global access, and activities that can optimize user funds.
What is Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchange (DEX) is a peer-to-peer crypto asset exchange platform where users can trade crypto assets without third-party intermediaries. DEX operates on blockchain technology, and the transaction settlement process is done through smart contracts that run automatically.
On DEX, users can trade via a crypto wallet that interacts directly with the DEX platform’s smart contracts. Thus, users have full responsibility for the management of their funds.
Since the user has full control over managing and storing crypto assets, errors such as sending funds to the wrong address and losing private keys are the user’s sole responsibility.

As of August 2023, 891 DEXs are operating across the blockchain network. Uniswap is the largest DEX regarding total value locked (TVL) at 3.6 billion US dollars. Curve DEX, Pancakeswap, Balancer, SUN, and other DEXs follow it.
DEXs offer several activities on its platform that can maximize users’ funds. For example, users can trade crypto assets, earn interest from crypto staking, lend funds, become a liquidity provider, speculate on the market using derivatives, etc.
How Does Decentralized Exchange (DEX) Work?
Users need to have in-depth knowledge of using DEX. The user experience on DEX is a bit more complex than centralized exchange (CEX). CEX is a crypto asset exchange platform operated by a central entity.
There are several types of DEXs designs available today. However, there are two types of DEXs are the most popular and most widely used by crypto users, namely DEXs with order book mechanisms and Automated Market Makers (AMMs).
DEX aggregators are also widely used by crypto users. DEX aggregators function to find the optimal price by comparing prices from various DEXs. In addition to paying attention to prices, DEX aggregators also compare gas fees charged.
Order book
The order book is a system that collects records of open buy and sells orders in the market in real-time. DEXs with fully on-chain order book systems are generally less popular due to several problems. Some of them include the need for high throughput and relatively high cost.
However, along with developing scalability solutions such as layer 2 with optimistic rollups and ZK rollups technology, on-chain order book DEXs are becoming more popular among crypto users.
Nevertheless, the more popular system is the hybrid order book. With this system, DEXs perform order matching off-chain while settlement remains on the blockchain (on-chain). Examples of DEXs with order book mechanisms are 0x, dYdX, Loopring DEX, and Serum.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
AMMs are the most widely used DEX mechanism, allowing users to access liquidity directly and become liquidity providers (LPs). LPs are an important part of the AMM mechanism as they work as providers of crypto assets for trading.
AMMs were created to address liquidity issues and use blockchain oracles to determine the traded asset’s price.
Users can directly buy or sell crypto assets through the liquidity pool, while liquidity providers (depositors into the AMM liquidity pool) can earn passive income from trading fees.
Some examples of DEXs with AMM mechanisms are Uniswap, Balancer, Aave, Curve, and others.
Read the full article What are Automated Market Makers (AMMs)?
To swap tokens, you can connect your crypto wallet to the DEX platform, then select the crypto asset you want to swap. For example, you have ETH and want to exchange it for SOL. You can input the amount you want to swap, then click Swap.
What is The Difference between DEX and CEX?
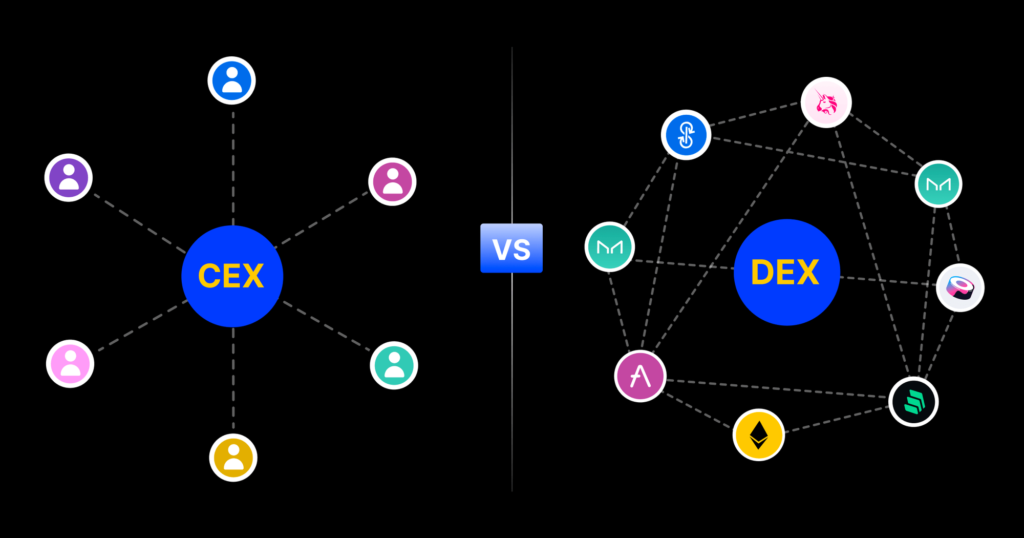
As mentioned above, a centralized exchange (CEX) is a crypto asset exchange platform operated by a central entity. Users must deposit their assets into an exchange account to buy and sell crypto assets. The CEX manages transactions and trade settlements through its internal system.
Some examples of CEXs we know include Pintu, Coinbase, Binance, OKX, Gemini, and others.
The difference between DEX and CEX lies in their operation and structure. DEX is a decentralized exchange platform that facilitates direct user trading through blockchain technology and smart contracts, giving users full control over their assets and high transparency.
On the other hand, CEX is run by a central entity, requires users to give control of assets to the exchange, and may have lower transparency depending on the exchange’s policies.
While DEXs offer the advantages of privacy and lower involvement in regulation, CEXs can process transactions faster and are easy to use.
The choice between the two depends on the user’s preference for asset control, transparency, speed, and regulatory compliance.
Advantages of Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- Full Control of Assets: One of the main advantages of DEXs is that users have full control over their assets. Users do not need to deposit their funds into an exchange account. It can increase security by avoiding the risk of exchange hacking or unexpected account closure.
- Transparency: All transactions in DEXs are recorded in a decentralized ledger that anyone can access. It increases transparency and openness, reducing the risk of data manipulation or false information.
- Convenience and Privacy: DEXs do not require users to disclose personal information such as KYC (Know Your Customer). It can maintain users’ privacy while allowing them to participate in crypto asset exchanges.
- Global Access: Since DEXs have no specific geographical or regulatory restrictions, anyone worldwide can access and trade on the platform.
Risks of Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- Low Liquidity: Some DEXs may face lower liquidity issues than CEXs, especially on less popular trading pairs. It may cause slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual price) on large trades.
- Vulnerability of Smart Contracts: Blockchain is considered secure for financial transactions, but the quality of the code in smart contracts depends on the development team’s expertise. The risk of bugs, hacks, vulnerabilities, and exploitation of smart contracts can threaten DEX users. Developers can mitigate these risks with security audits and code checks.
- Complex User Experience: Using DEXs can be more complicated for users without crypto experience. Processes such as using smart contracts, setting gas fees, and network selection require a deeper understanding.
Challenges and Future of DEX:
Like all innovations, DEXs come with their own set of challenges. The speed and efficiency of transactions in DEXs are currently still a concern. In addition, when there are problems with transactions or errors in smart contracts, recovering funds can be more complicated than CEXs.
Nonetheless, DEXs have great potential to change how crypto exchanges operate, giving more control to users and less reliance on central entities.
With the continued development of blockchain technology and a better understanding of digital security, DEXs will probably continue to take center stage in the crypto ecosystem.
Buying Crypto Assets on Pintu App
You can invest in crypto assets such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others without worrying about fraud on Pintu. In addition, all crypto assets on Pintu have passed a rigorous assessment process and prioritize the principle of prudence.
The Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets, such as Metamask, to facilitate transactions. Download the Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your safety is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to making transactions on the Pintu app, you can learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles that are updated weekly! All Pintu Academy articles are created for educational and knowledge purposes, not as financial advice.
References
- Tom Dunleavy, Decentralized Exchange Fundamental Analysis and Relative Value Comparison, Messari, accessed 16 Agustus 2023.
- Chainlink Team, What Is a DEX (Decentralized Exchange)? Chainlink, accessed 16 Agustus 2023.
- Cointelegraph Team, What are decentralized exchanges, and how do DEXs work? Cointelegraph, accessed 16 Agustus 2023.
- Benedict George, What Is a DEX? How Decentralized Crypto Exchanges Work, Coindesk, accessed 16 Agustus 2023.
- Cryptopedia Staff, What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)? Cryptopedia, accessed 16 Agustus 2023.
Share
Table of contents