What is Danksharding?

Ethereum just completed the Shapella update on April 12, 2023. Ethereum users can now withdraw and add to their staking at any time. With Shapella, Ethereum’s staking infrastructure is complete. Shapella also marks the first major Ethereum update since the network’s migration to the PoS system in September 2022. However, many in the crypto community are already talking about Ethereum’s next upgrade, EIP-4844. EIP-4844 is a proto-Danksharding that is rumored to be implemented by the end of 2023. So, what is Danksharding? Why is it called Proto-Danksharding? What about the potential impact of this upgrade? This article will explain it in detail.
Article Summary
- ⚙️ Ethereum completed the Shapella upgrade in April 2023 which allows users to withdraw or add to their staked ETH.
- 🗣️ The Ethereum community is already talking about the next update, EIP-4844 or Proto-Danksharding, planned for the end of 2023. Danksharding is an update aimed at improving Ethereum’s scalability. With this technology, L2 rollup transactions will be decoupled from the main Ethereum network and stored in “blobs”, which will then be attached to transaction blocks.
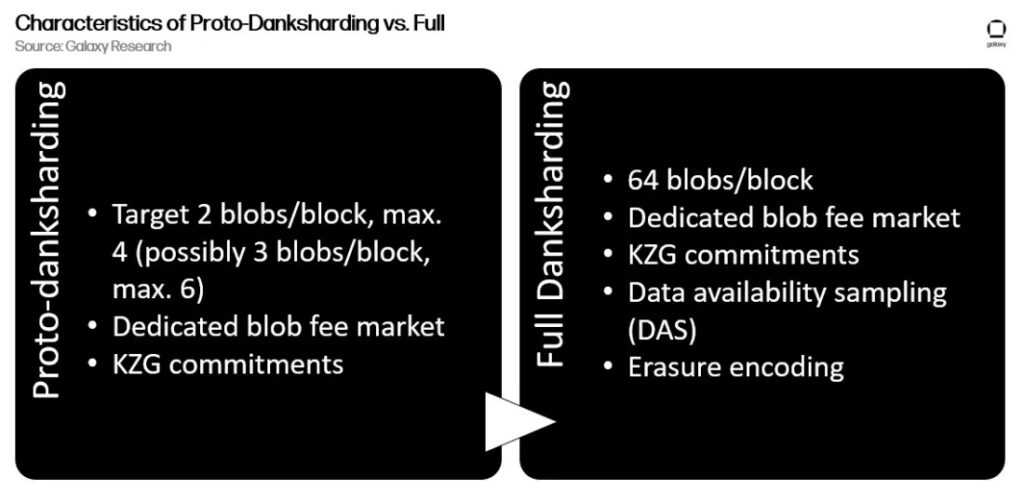
- 🧱 EIP-4844, or Proto-Danksharding, is the first stage towards a full implementation of Danksharding. This update will introduce various network modifications for blob transactions such as transaction processing logic, new verification rules, and a new fee market design.
- 📉 Proto-Danksharding allows for a significant reduction in L2 transaction fees. Blob transactions are initially free and gradually increase until they reach maximum capacity. Then, the consensus layer will store the blob data for three weeks and then delete it to prevent excessive data buildup.
- ⚖️ EIP-4844 has the potential to have a significant impact on L2 by reducing transaction fees. It could also be the catalyst for growth by driving more developers and users to the L2 sector.
What is Danksharding?
Danksharding is an Ethereum upgrade that will massively improve network scalability. Danksharding is an adaptation of sharding technology that has been modified specifically for Ethereum. The upgrade introduces a new type of transaction called “blobs”. These blobs are transactions from various L2 rollups. The blob will then be attached to a block as additional data separate from other transactions.
What is Sharding? Sharding is a technology that splits a blockchain into smaller pieces called shard chains. Each shard chain contains its own sets of validators that process different transaction data simultaneously. All shard chains communicate with each other to reach consensus and store data.
So, Danksharding essentially separates rollup transactions from regular Ethereum transactions. This plan is in line with Vitalik Buterin’s 2020 proposal (rollup-centric roadmap) which explains that Ethereum’s scalability will come from having more layer-2s connected to the main chain. Through Danksharding, all transactions from Ethereum’s L2 will have their own space that will attach itself to every block.
Danksharding is very different from typical sharding technology. Instead of separating the blockchain into multiple shard chains, Danksharding separates rollup transactions into blobs so as not to overload the main network. The Ethereum Danksharding implementation itself is still very far away (several years). Like The Merge, this upgrade will go through several stages starting with EIP-4844 or Proto-Danksharding.
What is EIP-4844?

EIP-4844 is the EIP name for the Ethereum Proto-Danksharding update. The name Proto-Danksharding itself was born from the names of two Ethereum core developers “Protolambda” and Dankrad Feist who proposed Danksharding. EIP-4844 is the first stage towards full Danksharding. So, Proto-Danksharding will lay the first foundation for full Danksharding by introducing new transaction types, transaction processing logic, new verification rules, and new fee market design. Proto-Danksharding will also make all rollup transactions cheaper. Furthermore, EIP-4844 will be in the Dencun (Deneb+Cancun) upgrade in late 2023.
Ethereum’s upgrade system post The Merge has slightly changed. All network updates will be done separately for the execution and consensus layers. In the case of Dencun, Deneb is the name for the consensus layer upgrade while Cancun is for the execution layer.
What are the Other EIPs in Dencun Update?
Deneb (Consensus Layer)
- EIP-4844 (Deneb and Cancun): Proto-Danksharding that will introduce blob transaction types.
- EIP-4788 (Deneb and Cancun): Opens information about the block root of the Beacon Chain to the EVM. This EIP opens up access to chain state in EVM for DApps development teams.
- EIP-7044: An update that ensures the signed validator exit will always be valid.
- EIP-7045: Increased the maximum inclusion range of attestation slots from one epoch to two epochs. This update improves the security of Ethereum.
Cancun (Execution Layer)
- EIP-5656: An update that introduces a new instruction code in the EVM to allow developers to locate specific memory areas. This is useful for protocols that require intensive computation.
- EIP-1153: Introduces operational code for transient storage. With this, transient storage data will be automatically deleted after the transaction is complete. This update opens up new uses for applications that require this feature.
- EIP-6780: Changed the function of the opcode
SELFDESTRUCTto automatically move all assets to the account operating the code unless done in the same transaction. This code is used to delete and create smart contracts.
How does Proto-Danksharding Work?
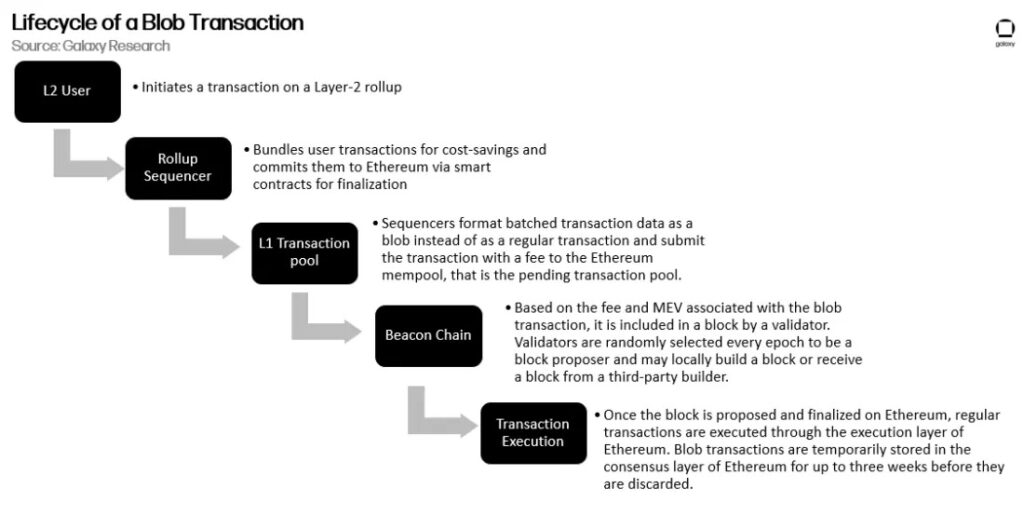
Proto-Danksharding is the first stage towards full Danksharding of Ethereum. It begins by introducing blob, also known as blob-carrying transactions. Blob-carrying transactions are separate from regular Ethereum transactions. So, Ethereum is also designing a fee market specifically for blob transactions. The illustration above is how Ethereum and the L2 sequencer process blob transactions. Additionally, there are some interesting things about blob transaction processing.
The blob transaction fee itself is initially free and will increase until it reaches its maximum capacity (current agreement 4 blobs/transaction or 512kb). However, Proto-Danksharding will still reduce L2 transaction fees significantly (100-900%) but the Ethereum team doesn’t have an exact estimate yet (some argue it will be up to 20x cheaper).
Another interesting thing about blob transactions is that the consensus layer will store the blob data for three weeks and then delete it to prevent excessive data buildup. There is a time delay in case there are incorrect or invalid transactions. However, Layer 2 can still store transaction data off-chain if they wish. The temporary state of blobs also saves storage space for Ethereum and makes all blob transactions cheaper than regular transactions.
Finally, since Proto-Danksharding is part of the full Danksharding implementation, the Ethereum team is developing the KZG Commitments system. Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg (KZG) commitments are a type of Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) that allows verification of polynomials without revealing the entire polynomial. Since blobs are quite large, KZG Commitment is a way to verify blobs without the need to read all the data. Like the ZKP system, verifying KZG commitments involve cryptographic computation.
So, processing KZG Commitment requires a secret set of random numbers through a trusted setup system called KZG Ceremony. The KZG Ceremony is basically Ethereum’s way of getting all its users to contribute their secret numbers for reading KZG Commitment. You can also contribute through the KZG Summoning Ceremony website.
Confused by the KZG Commitment explanation? Read the Zero-Knowledge article first at Pintu Academy.
Impact and Potential of EIP-4844

EIP-4844 or Proto-Danksharding could potentially have a huge impact on L2. The figure above describes four main benefits of Danksharding and EIP-4844. The first two are specific to L2 like Arbitrum and Optimism. While their transaction fees are below Ethereum’s, network density still causes significant volatility in transaction fees. Data from Tokenterminal also shows that 75% of transaction fees on Arbitrum are paid to Ethereum validators. With EIP-4844, the fees that developers have to pay to run L2 will drop dramatically.
EIP-4844 also has the potential to be a significant catalyst for Ethereum’s L2 sector. Lower transaction fees could be a major factor in attracting more developers and users to L2 protocols. On top of that, Optimism and Arbitrum are also building their own infrastructure with Optimism Stack and Arbitrum Orbit. Polygon’s efforts to overhaul its ecosystem with Polygon 2.0 will also create a highly competitive sector.
If the implementation of Dencun and Proto-Danksharding goes smoothly, we will likely see an L2 war on Ethereum. It’s also not impossible to see more new L2s popping up post-EIP-4844. With that in mind, the Dencun upgrade will be a very interesting opportunity for investors in Ethereum and L2 projects.
Conclusion
On April 12, 2023, Ethereum completed the Shapella update which gave users more freedom in staking their ETH assets. Now, the crypto community’s attention shifts to the next update, which is EIP-4844 or Proto-Danksharding, scheduled for the end of 2023. EIP-4844 is the first stage towards Danksharding, a massive update that aims to improve Ethereum’s scalability. Through Danksharding, rollup transactions will be separated from regular Ethereum transactions and stored in blobs, allowing for significantly reduced transaction fees. EIP-4844 is the foundation that will introduce blob transactions and how they are processed. This update also includes a series of other EIPs aimed at improving and enhancing Ethereum’s performance. If successful, these updates could spur the growth of Ethereum’s Layer 2 sector and attract more developers and users.
How to Buy ETH Coin in Pintu
You can start investing in ETH and buy it on the Pintu app. Here is how to buy crypto on Pintu:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for ETH.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you are a crypto investor!
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Go and download the Pintu cryptocurrency app on Play Store and App Store! Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
You can also learn crypto through the various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- Danksharding | ethereum.org, accessed on 26 June 2023.
- DFG Official, Ethereum Dencun Upgrade: The Next Big Enhancing in Scalability, Medium, accessed on 27 June 2023.
- Christine Kim, Ethereum All Core Developers Consensus Call #111 Writeup, Galaxy Research, accessed on 27 June 2023.
- Christine Kim, Ethereum All Core Developers Execution Call #164 Writeup, Galaxy Research, accessed on 27 June 2023.
- Christine Kim, Proto-danksharding: What It Is and How It Works, Galaxy Research, accessed on 28 June 2023.
- Vitalik Buterin, Proto-Danksharding FAQ – HackMD, Ethereum.org, accessed on 28 June 2023.
- @blockworkres, “Rollups are becoming increasingly important for Ethereum to reach mass adoption.”, Twitter, accessed on 28 June 2023.
Share